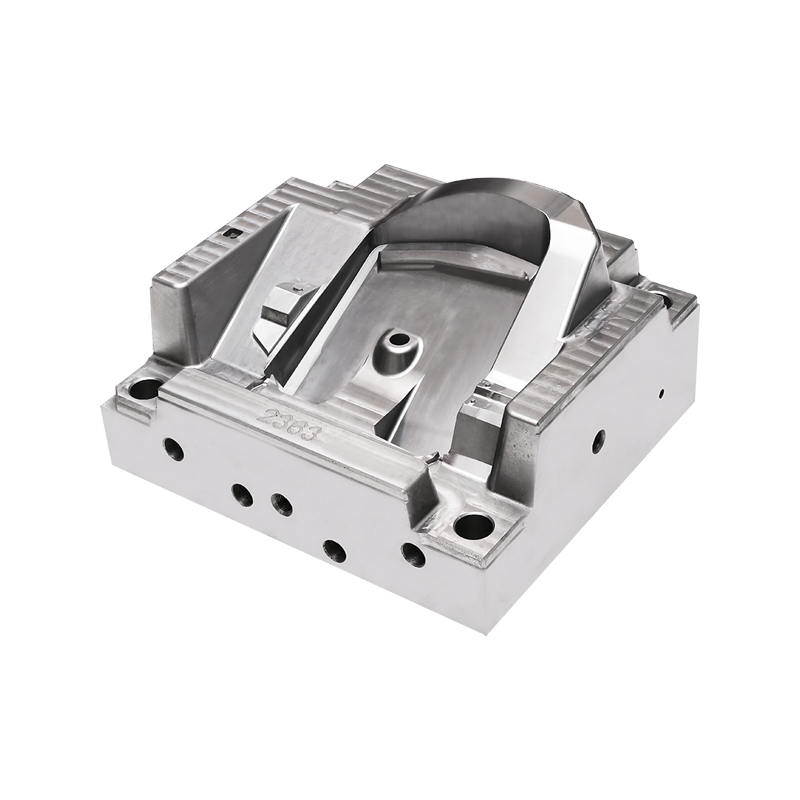
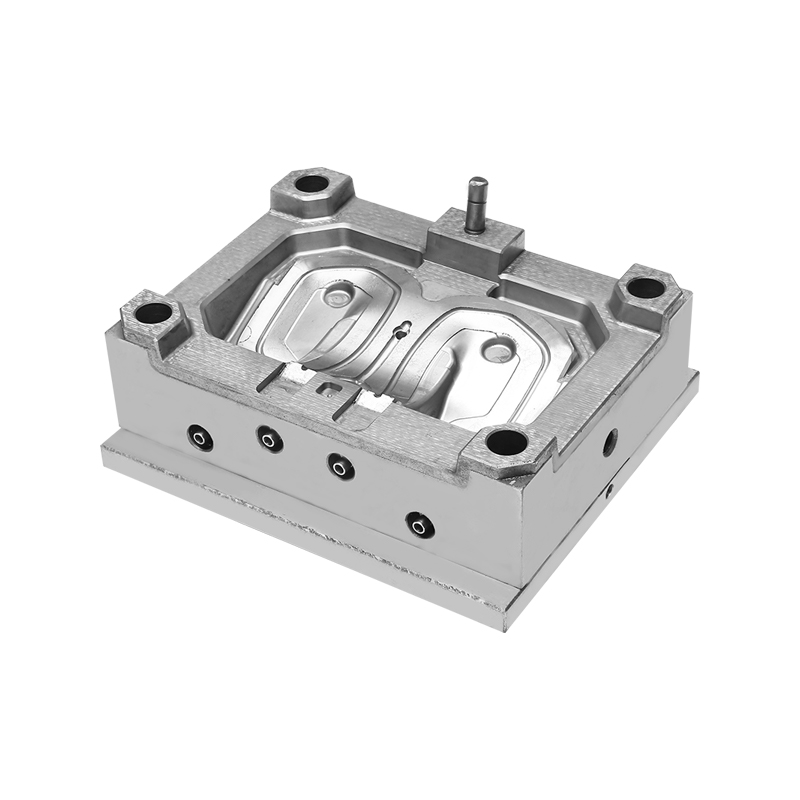
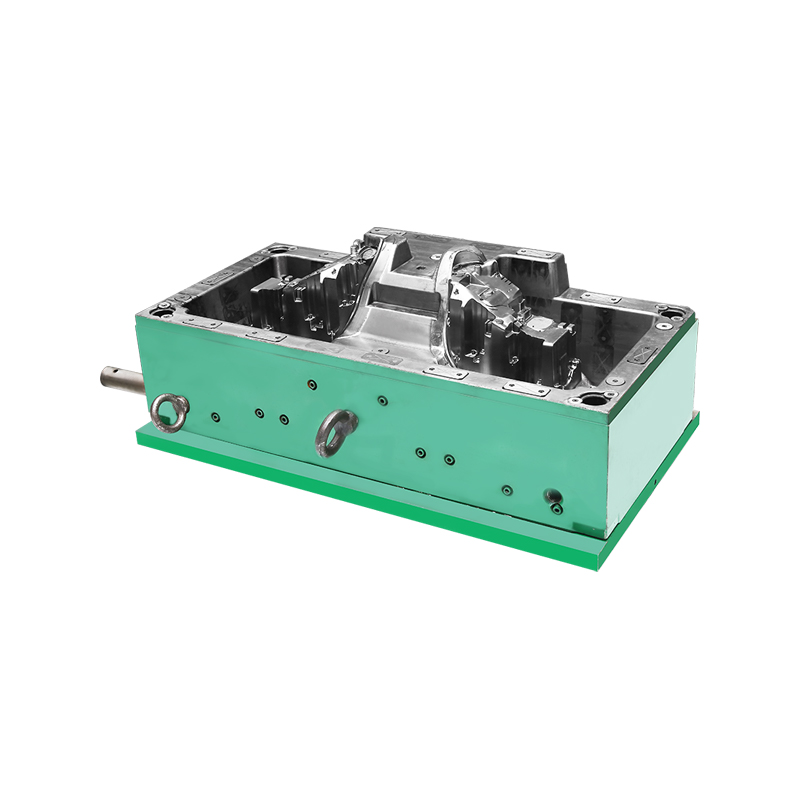
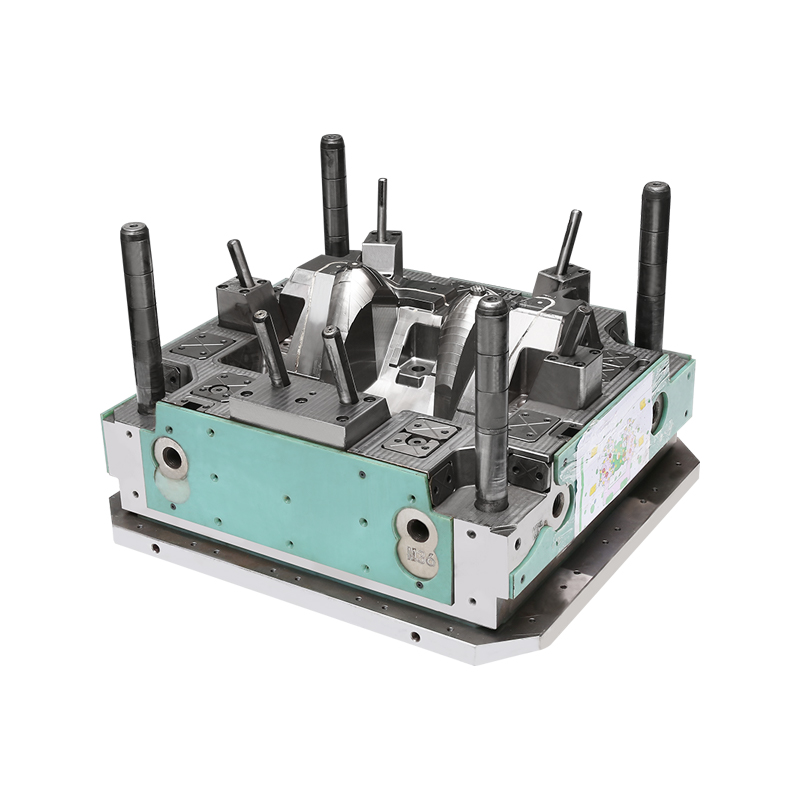
Bulk Molding Compound, commonly referred to as BMC, is a thermoset composite material composed of resin, glass fibers, fillers, and additives. When combined with carefully designed molds, BMC enables the production of complex components that meet mechanical and dimensional requirements across many sectors. The continued adoption of BMC Mold solutions reflects broader changes in how manufacturers approach composite material processing and long-term product performance.
One reason BMC Mold attracts attention is its ability to support stable and repeatable production. BMC materials flow well during the molding process, allowing molds to fill evenly even when parts feature ribs, inserts, or varying wall thicknesses. This consistency helps manufacturers reduce variation between parts and maintain predictable output over extended production cycles. In industries such as electrical equipment, automotive components, and infrastructure systems, this level of reliability supports smoother assembly and fewer downstream adjustments.
Design flexibility also contributes to the appeal of BMC Mold systems. Engineers can integrate multiple functional elements into a single molded part, reducing the need for secondary operations. Threaded inserts, mounting points, and structural reinforcements can often be molded directly into the component. This integration supports more compact product designs and simplifies supply chains, which is increasingly important as manufacturers aim to streamline production while maintaining functional requirements.
Material performance is another factor driving interest in BMC Mold technology. BMC parts typically demonstrate good dimensional stability, electrical insulation properties, and resistance to heat and corrosion. These characteristics make them suitable for applications where environmental exposure or thermal stress is a concern. Electrical enclosures, switchgear housings, and automotive under-hood components frequently rely on BMC Mold solutions to meet both functional and regulatory expectations.
The mold design process plays a critical role in achieving these outcomes. BMC Mold development requires careful consideration of material flow, venting, and curing behavior. Unlike some thermoplastic processes, BMC molding involves a curing reaction that transforms the material into a rigid structure. Mold makers must account for this behavior to ensure complete filling and uniform curing throughout the part. Advances in simulation software have helped mold designers predict flow patterns and optimize cavity layouts, contributing to more efficient development cycles.
Sustainability considerations are also influencing how BMC Mold systems are designed and used. Manufacturers are exploring ways to reduce material waste, improve energy efficiency during molding, and extend mold service life. Durable mold construction and precise process control help minimize scrap rates, supporting more responsible use of raw materials.
BMC Mold applications continue to diversify. Construction-related components, transportation systems, and renewable energy installations increasingly rely on composite materials that can withstand demanding conditions. BMC Mold technology offers a balance between mechanical strength and design adaptability, making it suitable for both established and emerging uses. This adaptability allows manufacturers to respond to shifting demand without overhauling their entire production infrastructure.
Quality control remains a central focus in BMC Mold production. Consistent material preparation, accurate temperature control, and well-maintained molds all contribute to stable output. Many manufacturers invest in inspection systems and process monitoring tools to ensure that molded parts meet defined specifications. These practices help build confidence among customers who depend on predictable performance from composite components.
In this context, BMC Mold serves as a practical solution that bridges traditional molding techniques and modern composite requirements. Its role in industrial production highlights how thoughtful material and mold design can support long-term manufacturing goals.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español








