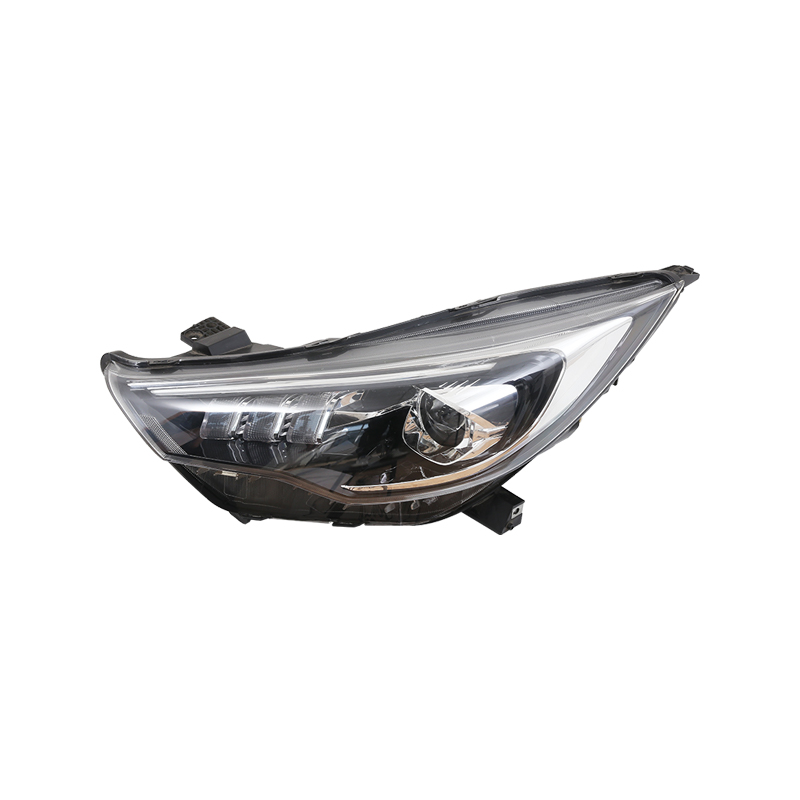
Car body moulds are essential tools in the automotive manufacturing process, providing the precise shapes and forms needed to produce vehicle panels and components. The choice of material for these moulds significantly affects their performance, durability, and the quality of the final product. Understanding the types of materials used in car body moulds helps manufacturers select the right solution for their production needs.
Steel: The Common Choice
Steel is the widely used material for car body moulds due to its strength, durability, and wear resistance. High-quality tool steels, such as H13 or P20. are often selected for moulds that must withstand repeated stamping or pressing. Steel car body moulds can maintain precise tolerances over long production runs, making them ideal for high-volume automotive manufacturing.
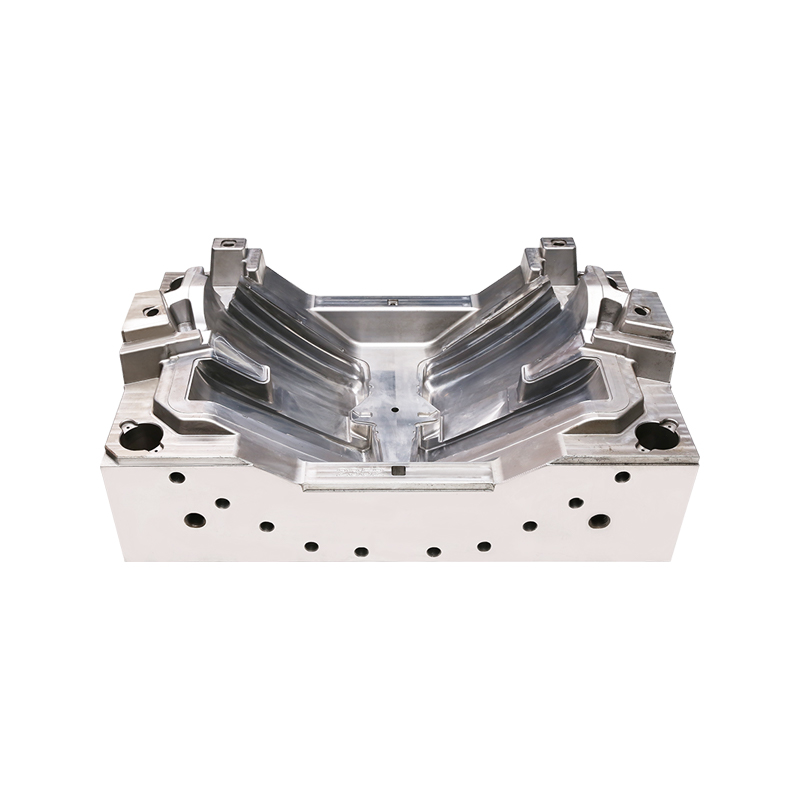

One advantage of steel is its ability to handle high pressure without deforming. For large vehicle panels, where exact shape replication is critical, steel car body moulds ensure consistent results. Additionally, steel can be heat-treated to increase hardness, extending the mould’s lifespan.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Easy to Machine
Aluminum is another material used in car body moulds, particularly for prototype or low-volume production. Aluminum is lightweight, which makes the moulds easier to handle and reduces tooling costs. It also allows faster machining compared to steel, enabling quicker turnaround for design testing or modifications.
While aluminum car body moulds are less durable than steel, they are suitable for situations where speed and flexibility are prioritized. Automotive engineers often use aluminum moulds for prototypes, where multiple design iterations are expected before committing to steel tooling.
Composite Materials: Innovation in Car Body Moulds
In recent years, composite materials have gained attention in car body moulds. Carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) and other composite materials can be used to produce lightweight moulds with high strength-to-weight ratios. These materials are particularly useful for low-volume or specialized components, where traditional steel or aluminum may not be cost-effective.
Composite car body moulds can also reduce production time and energy consumption. Their use is expanding in electric vehicle manufacturing and in industries where sustainability and efficiency are becoming more important.
Other Considerations in Material Selection
Choosing the right material for car body moulds depends on several factors, including production volume, part complexity, and budget. Steel is preferred for high-volume production due to its longevity, while aluminum or composite moulds are ideal for prototypes or small batches. Manufacturers also consider the type of stamping or forming process, as different operations may place varying stresses on the mould.
Surface finish is another important consideration. Some materials allow smoother surfaces, reducing the need for additional finishing on the car body panels. Proper material selection ensures that car body moulds deliver precise shapes, reduce defects, and improve overall manufacturing efficiency.
The materials used for car body moulds play a crucial role in the quality, efficiency, and cost of automotive production. Steel remains the dominant choice for high-volume applications, while aluminum and composite materials provide flexibility for prototypes and specialized components. By understanding the characteristics of each material, manufacturers can select the solution to meet design requirements, production needs, and budget constraints.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español








